By Matt Walker
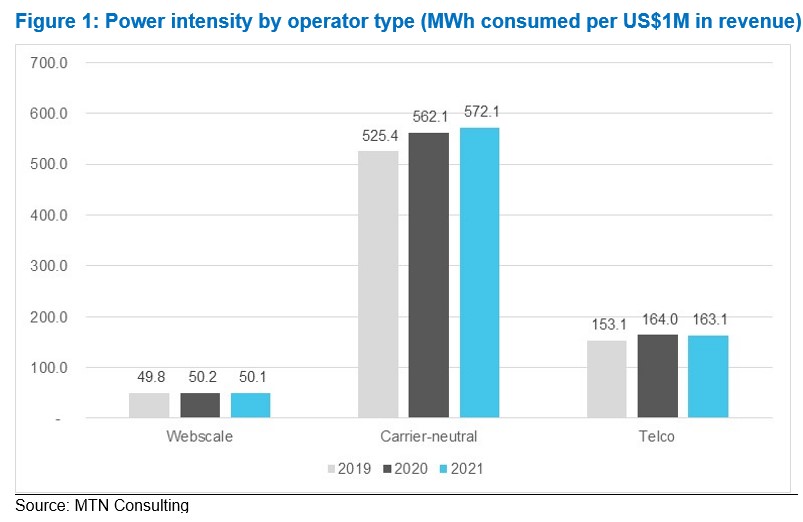
This brief presents data on energy spending by operators of cell towers, data centers, and fiber networks, and discusses the implications of the data and likely future directions. Utilities represent a large portion of operating expenses for these infrastructure-focused companies, which we track as “carrier-neutral network operators” (CNNOs). CNNOs also spend more than other types of operators. Webscale spending on power is miniscule relative to their size, less than 1% of opex (ex-D&A). Telcos spend a few % of opex (ex-D&A) on utilities. But CNNOs can spend more than 30% and up to 80% of opex (ex-D&A) on utilities.
- Table Of Contents
- Figures and Tables
- Coverage
- Visuals
Table Of Contents
- Summary – page 2
- CNNOs are more energy-intensive than other operator types – page 2
- Sustainability in networks needs to start with CNNOs – page 4
- Implications – page 5
- Appendix – page 6
Figures and Tables
Figure 1: Power intensity by operator type (MWh consumed per US$1M in revenue)
Figure 2: Utilities spend as a % of opex (excluding depreciation & amortization), 2020-22
Figure 3: Utilities vs. D&A costs as a percentage of total opex, 2022
Coverage
Companies mentioned:
America Movil
AT&T
Bharti Infratel (Indus)
Cellnex
China Tower
ChinData
Chorus Limited
Ciena
Crown Castle
CyrusOne
Digital Realty
GDS Data Centers
Helios Towers
IHS Towers
QTS Realty
Sarana Menara Nusantara
Switch
TDF Infrastructure/Arcus
Telefonica
Teraco
Verizon
Visuals