By Matt Walker
This brief is a short profile of India’s Centre for Development of Telematics (CDOT).
CDOT is a widely misunderstood “public sector undertaking” (PSU) of the Indian government. It presents itself as a stodgy, outdated agency with limited relevance to fast-paced modern communications networks. It has almost no marketing or public relations function. Its website is badly outdated; the organizational timeline outlined on its site stops in 2016, for instance. Many of the products it makes available to partners through ‘transfer of technology’ (TOT) or commercialization agreements are similarly dated, and not competitive with offerings from private sector players such as Cisco, Ericsson, and Nokia. But there is far more than meets the eye. CDOT has upped its game in the last few years, boosting its speed and profile under the current CEO, Rajkumar Upadhyay, who took over in 2022. CDOT oversees the government’s Telecom Technology Development Fund “TTDF”, a small fund which is broadening its reach and budget over time. CDOT has been investing in 5G tech development alongside the big 4G project it’s currently implementing at state telco BSNL, in collaboration with Tata Consultancy Services. While 4G may be yesterday’s news, CDOT is working on 5G with several startups, including Galore, VVDN, and WiSig. CDOT is also central to India’s efforts to develop capabilities in quantum communications and cryptography, and hosts an annual “conclave” on the topic. Relatedly, CDOT tech is essential to the operations of India’s government and defense communications networks, which will ensure the agency have ongoing budgetary support. Its current budget is tiny: in the fiscal year ended March 2023, its total expenses amounted to just $68M. That works out to about 1.5% of the $4.7B Ericsson spent just on R&D in the same timeframe, or 18% of the US FCC’s total budget was for that 12 month period. CDOT is getting a lot of bang for this relatively small investment of bucks. And there are many signs that point to the entity playing a bigger role over time as a facilitator in the telecom side of Make in India.
- Table Of Contents
- Figures and Tables
- Coverage
- Visuals
Table Of Contents
- Summary – page 2
- CDOT overview – page 2
- Introduction – page 2
- Financial position – page 4
- Technology development and diffusion – page 6
- Transfer of technology (ToT) & commercialization partnerships – page 6
- Other vehicles for CDOT influence on telecom technology – page 7
- Areas of focus: 5G and Quantum – page 8
- 5G – page 8
- Quantum Communications – page 9
- Outlook and recommendations for CDOT – page 12
- Outlook – page 12
- Recommendations for CDOT – page 14
Figures and Tables
Figures:
- Figure 1: CDOT revenues vs. expenses
- Figure 2: CDOT inflows – revenues and government “contributions”
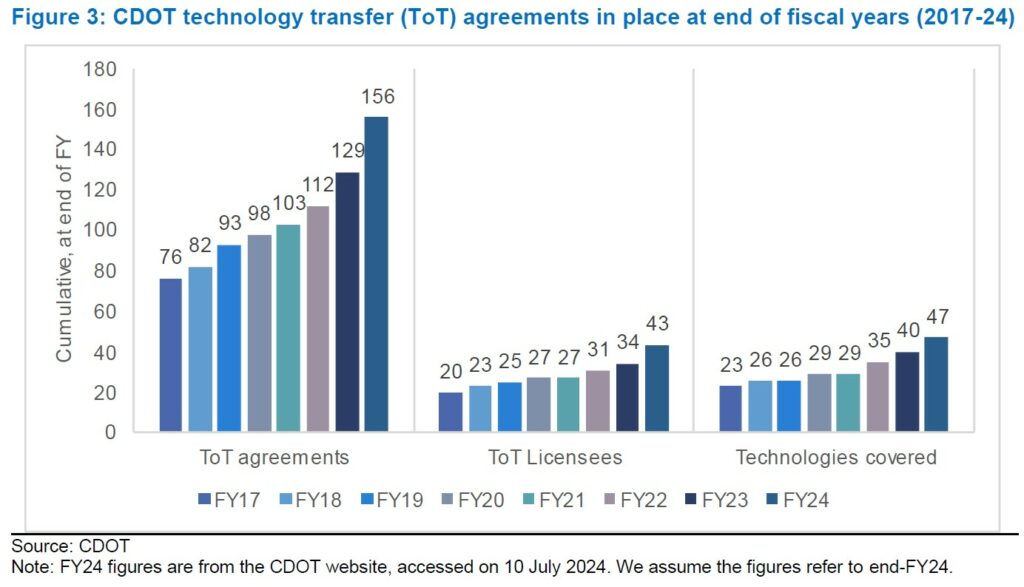
- Figure 3: CDOT technology transfer (ToT) agreements in place at end of fiscal years (2017-24)
- Figure 4: CDOT’s 5G Alliance – 10 consortia
- Figure 5: CDOT CEO speech at QC Conclave in 2024 – Self-reliance a focus
- Figure 6: Telco NI market shares in 2023 of key China- and India-based tech vendors
Tables:
- Table 1: Key facts about CDOT (2024)
Coverage
Organizations mentioned:
Aggressive EMS
Airtel
Arista Networks
Astra Microwave
Bharat 6G Alliance
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
Bharatnet
BSNL
Centre for Development of Telematics (CDOT, or C-DOT, or C-DoT)
Cisco Systems
Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL)
Ericsson (Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson)
Fortinet, Inc.
G-20 Digital Economy Working Group
Galore Networks
GoIP Global Services
HFCL Limited
Huawei Technologies
India 5G Alliance
India Department of Space
India Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
India Dept of Defense
India Digital Communications Commission (DCC)
India National Security Council Secretariat for R&D.
India Physical Research Laboratory (PRL)
India Quantum Alliance
India Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC)
India Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC).
India Telecom Technology Development Fund
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) at: Bombay, Jodhpur, Kanpur, Madras, Roorkee
Indian Telephone Industries Limited (ITIL)
Instrumentation Kota
Jio Platforms
Juniper Networks
Lekha Wireless
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Mauritius Telecom
MTNL
Nivetti Systems
Nokia Corporation
Precision Electronics Limited (PEL)
Qualcomm Technologies
RailTel
Resonous Technologies
Saankhya Labs
San Diego State University – Multimedia and Wireless Networks Research Group
Signalchip
Signaltron
Sooktha Consulting
Surabhi Satcom
Tata Consultancy Services
Tech Mahindra
Tejas Networks
Telecom Centres of Excellence India (TCOE India)
Telecom Consultants of India Limited (TCIL)
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI)
Terra Quantum
United Telecoms Limited (UTL)
USA NASA
USA NSA
Vi (Vodafone India)
VVDN Technologies
WiSig Networks
Visuals