By Arun Menon
Telcos worldwide are finally getting onboard the 5G bus, delivering high speeds with low-latency and seamless experience to enterprises and consumers. The latest connectivity standard presents growth and monetization opportunities for telcos with new services targeting a wide range of vertical markets. However, telcos’ inability to convert these opportunities into major new revenue streams so far has held back industry growth.
One of the biggest concerns telcos face today is to keep profitability ticking amid the immense burden of investments, stagnating revenues, macro pressures worsened by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and fierce competition from new-age operators. The success of telcos in the 5G era will depend on unlocking value and efficiencies through cost optimization measures, thus ensuring a continuous flow of investments and profitability. This is not new for telcos, as they have been able to deliver steady profitability margins amid flat to slight revenue growth environments for the past several years. To do this, they resorted to traditional means of cutting costs in the past mitigation cycles, efforts which have been narrow and tactical in nature. These included asset sell-offs, real-estate rationalization, repair and maintenance outsourcing, shared services models, etc.
With uncertain macro-factors at play, telcos will find it much harder to optimize costs through traditional tactics alone. To drive sweeping changes going forward, telcos will have to implement dramatic, strategic measures to optimize their cost structure in order to increase and sustain profitability. These strategic measures will be a mix of technology-enabled solutions and collaborations, some of which will transform the telco business model. Each of the cost optimization measures target multiple cost centers to deliver savings. Listed below are five key strategic cost optimization measures telcos will implement over the next 2-3 years:
- Automation: Automation will be a key enabler to achieve savings in cost areas such as networks (through automated fault detection and self-optimization systems, for instance), energy (dynamic shutdown of unused network elements during idle time), sales and marketing (virtual assistants for customer support and experience), and G&A (admin tasks automation).
- Open RAN/vRAN: Telcos could explore reducing multiple cost bases using open interface-based technology solutions such as Open RAN and vRAN. These may offer reduced network-related costs such as infrastructure rentals, RAN power consumption, repair and maintenance, etc.
- Network sharing agreements: Telcos for many years have turned to sharing network elements among them primarily to save costs. The most common form of network sharing has been the joint use of cell sites, towers, backhaul transport networks, etc., called passive infrastructure sharing. This evolved to sharing of active network components in the recent years that includes RAN components and spectrum. To achieve further cost savings in the 5G era, telcos are exploring the sharing of core network components and functionalities (called “core network sharing”).
- Partnerships with webscale cloud providers: Through partnerships with cloud providers, telcos are reducing network costs by moving critical network functions and workloads to the cloud, saving energy costs by deploying custom-designed energy efficient hardware and architectures developed by cloud providers, and driving personalized marketing and customer experience by turning customer data into insights with cloud data and analytics.
- Network slicing: By segmenting parts of the network to cater to different customer types and use cases, network slicing will enable telcos to reduce opex costs through improved operations stemming from fewer cross-dependencies between network functions. This should also reduce maintenance costs as a result of isolated slices deployment, which shields disruptions in other part of the network.
While we expect these relatively new approaches to drive change going forward, telco cost mitigation will require a blend of traditional and broad strategic measures. The crux of any strategy will be to integrate or bring the various business functions closer instead of being siloed, to drive maximum cost efficiencies across the telco organization.
- Table Of Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Coverage
- Visuals
Table Of Contents
Summary – page 2
Telcos wrestle to keep costs in check amid stalled growth and macro pressures – page 3
Managing opex efficiently requires dissecting it further into standardized cost categories – page 5
For telcos, network-related costs alone account for ~50% of total opex – page 7
Group-wide efficiencies will depend on the control of overhead costs beyond networks – page 9
Telco labor costs are on the rise despite industry headcount reductions – page 12
New technology and partnerships are key tenets of telco cost savings in the 5G era – page 14
Traditional cost-saving measures continue – page 19
The mix of newer, more strategic cost cutting efforts and traditional approaches will vary with the operating climate – page 20
About – page 21
Figures
Figure 1: Operating margins: Global telco market, annual
Figure 2: Global telco revenue, YoY growth rate (%)
Figure 3: Telco capital intensity (Capex/Revenues), annualized
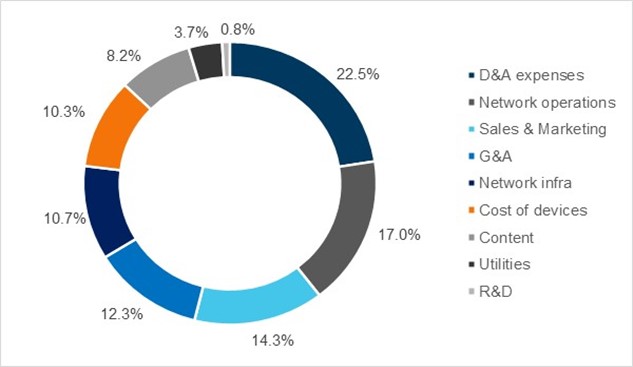
Figure 4: Opex items as a % of total opex, group of 30 telcos: Average, 2016-21
Figure 5: All network-related* opex, % total opex: Group of 30 telcos
Figure 6: Network-related opex categories as % of total opex: Group of 30 telcos
Figure 7: Telco-specific opex (non-network) as % of total opex: Group of 30 telcos
Figure 8: Non-telco-specific costs as % of total opex: Group of 30 telcos
Figure 9: Labor costs as a % of total opex: Group of 30 telcos
Figure 10: Labor costs per employee (US$K): Group of 30 telcos
Tables
Table 1: Automation’s impact on opex by cost area
Table 2: Network slicing’s impact on network operations opex
Table 3: Open RAN and vRAN impact on opex by cost area
Table 4: Network sharing impact on opex by cost area
Table 5: Cloud partnerships’ impact on opex by cost area
Coverage
Companies and organizations mentioned in this report include:
1&1 AG
Amazon
AT&T
Bharti Airtel
Bouygues Telecom
BT
Charter Communications
China Telecom
China Unicom
Comcast
Deutsche Telekom
Dish Network
Du
Ericsson
Etisalat
Globe Telecom
KDDI
KT
Microsoft
MTN
Netflix
Nokia
Ooredoo
Orange
Rakuten Mobile
Reliance Jio
ServiceNow
SK Telecom
Telecom Italia
Telefonica
Telenor
Telia
Telkom Indonesia
Telus
Turkcell
Verizon
Vodafone
Visuals